HABITATS AND LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS

BIODYSSEUS
SPARTAN SPACE works for the French polar explorer Alban Michon on the development of the BIODYSSEUS underwater station that will be installed in the Arctic.
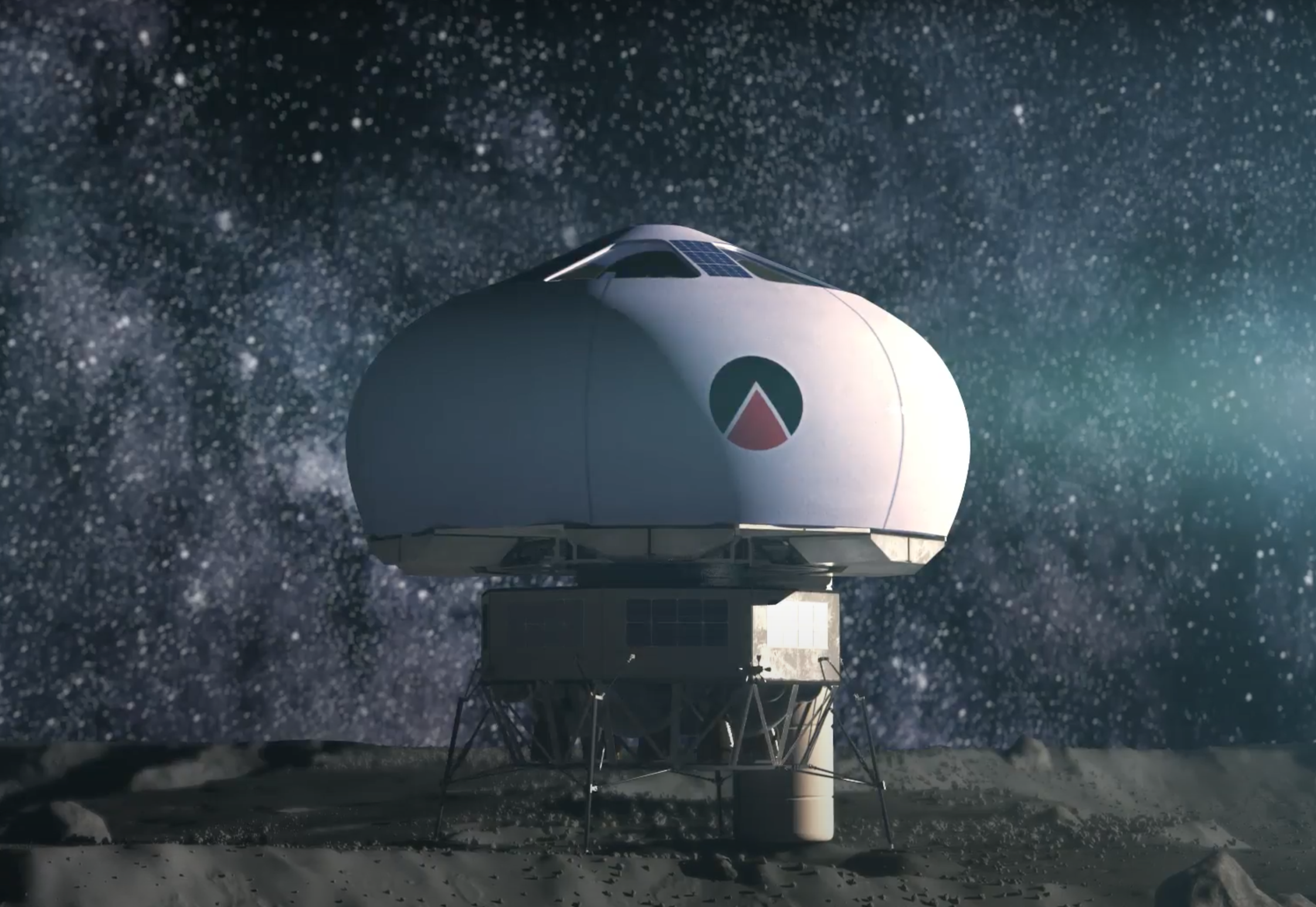

EUROHAB
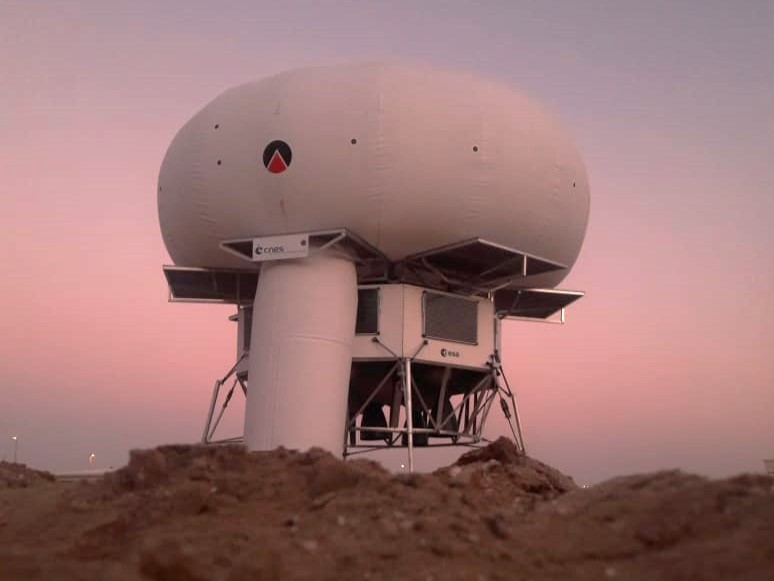
Peter WEISS and Jean-Jacques FAVIER, two of the co-founders of Spartan Space, developed the EuroHab concept, an inflatable habitat for missions on the surface of Moon or Mars. Late 2020, the EuroHab concept won the “Lunar village” special mention at the Jacques Rougerie Foundation – Institut de France International Architecture Competition. Following this award, a scaled prototype of the habitat was selected to be exhibited in the French pavilion during Expo 2020 Dubai starting in October 2021.
more on EUROHAB >>>>
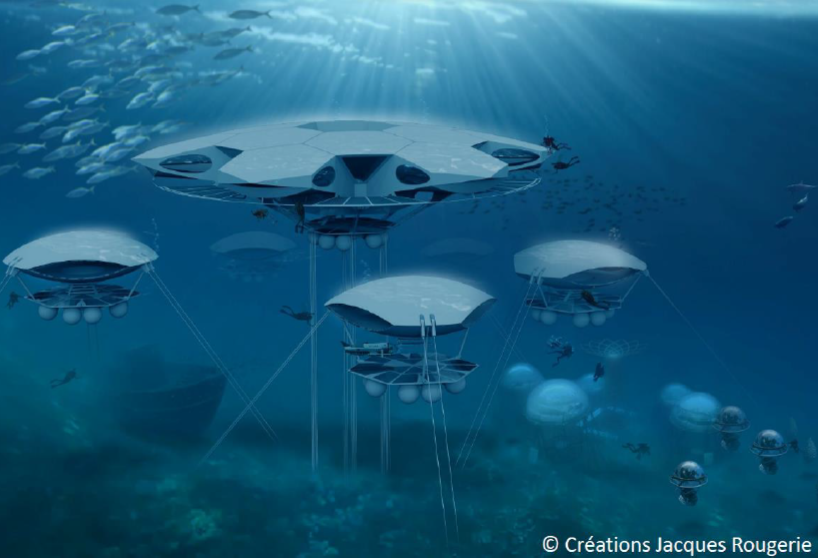

SUBSEA VILLAGE
The architect and oceanographer Jacques Rougerie initiates together with SPARTAN SPACE the development of an international subsea village dedicated to research, education and the development of the Blue Economy.
The concept of a permanent underwater campus would allow researchers, students and engineers to study and monitor in situ and continuously over long periods the subsea environment.

ILOTS
Spartan Space was under contract with CNES to manufacture the full-scale functional prototype of the EUROHAB concept. The prototype is designed to be used with the LDE mock-up.
L.I.S.E
The LISE (Lunar International Shelter for Exploration) project is a project initiated by the Spaceship France with the ambition to design a reusable lunar habitat to extend the exploration of the moon during the crewed missions on the surface of the Moon.
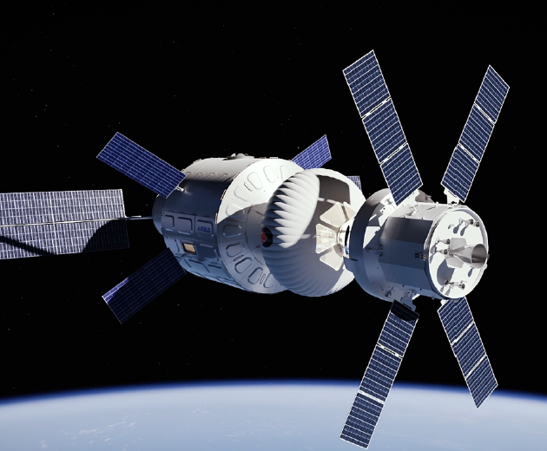

Orbital EUROHAB
Spartan Space was contracted by ESA under the EISI – ESA Initial Support for Innovation grant to propose technical and commercial approach to the Agency for post-ISS LEO services.
SIMULATION AND TRAINING
ROBOTIC LANDER PLATFORM SIMULATOR
SPARTAN SPACE developed under a contract with BPI a robotic lunar lander platform that can serve for simulations with rovers, charging stations or ISRU instruments.
The system is transportable for analogue trials worldwide and includes a power supply and communications interface to external elements. The top platform (diameter 4 meters) can serve to host payload and from where it can be lowered to the surface.
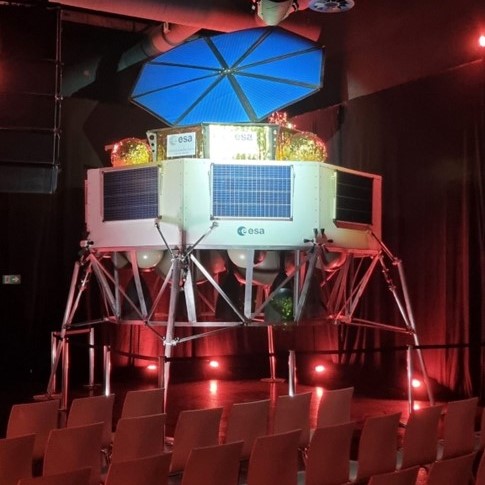

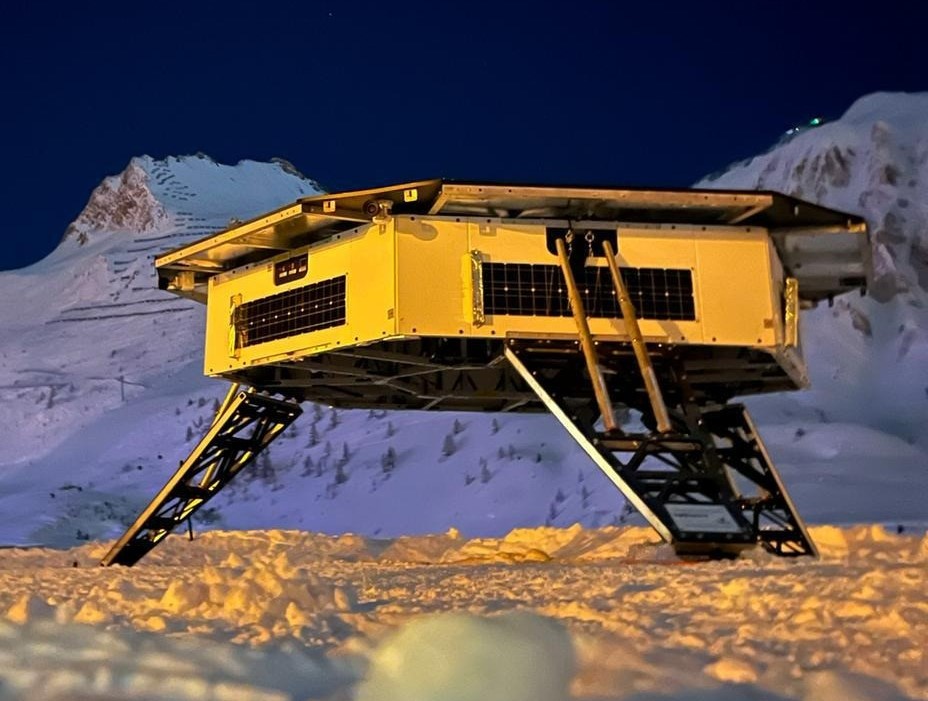
LDE Argonaut Project
Spartan Space was contracted with ESA in 2021 to develop a physical 1:1 mock-up of the Landing and Decent Element now known as Argonaut. Argonaut is Europe’s autonomous access to the Moon, allowing us to play a major role on the surface of our natural satellite. The lunar lander is being designed for a series of missions with many options for its payloads – from cargo and infrastructure delivery to scientific operations, a rover or a power station, Argonaut is being designed as a versatile access to the Moon. The mock-up was delivered to EAC, Cologne, and is being used at several exhibitions and conferences.
Along with the Argonaut mock-up, ESA contracted Spartan Space to build the ECSM – The European Charging Station Mock-Up as a payload for the Argonaut Mock-up. ECSM is for the Moon mission located on the moon’s surface and aims at providing power in the frame of the international lunar exploration architecture.
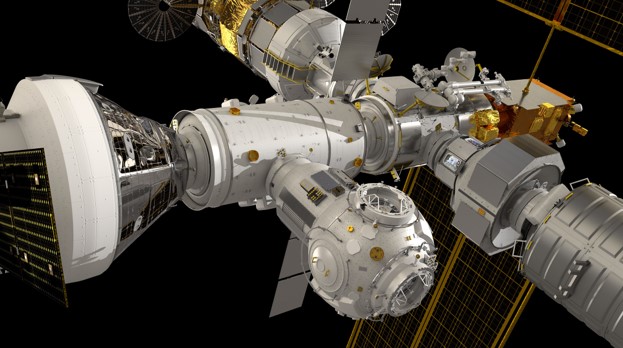
i-HAB
SPARTAN SPACE develops for THALES ALENIA SPACE under Liquifier Space Systems the human-in-the-loop model for ergonomic trials and astronaut training. The system will be scale one and be delivered to JSC in Houston for tests and training of the crew for operations on the I-HAB module on GATEWAY.

SUBCAVE (2022)
The objective of the Hungarian CAVE feasibility study is to carry out a comparison based on the prior state-of-the-art analysis to facilitate the ranking of the most promising candidate locations with a clear justification to conclude whether the Molnár János cave system or other Hungarian alternatives.
ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
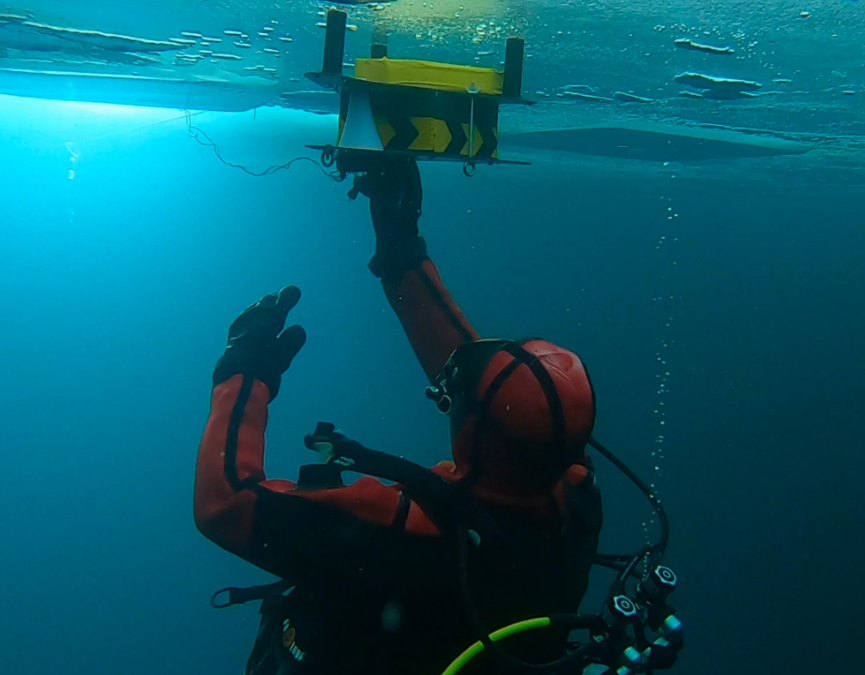


L.A.M.A (Lake Aquatic Monitoring Array)
is a subaquatic monitoring station designed for installation in extreme environments. It communicates via antenna with a ground station onshore, transmitting video, temperature, and water quality data.
The system’s capabilities can be expanded with additional sensors.
Developed by SPARTAN SPACE, LAMA underwent testing during an under-ice monitoring campaign at a high-altitude lake in the French Alps.
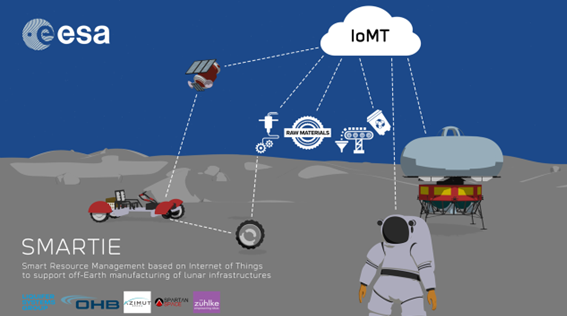
Smartie
is an ESA contract resulting from the OSIP call for ideas.
The project aims to develop a resource management data for IoT devices on the Monn. Spartan Space is a subcontractor to Liquifer Systems Group.
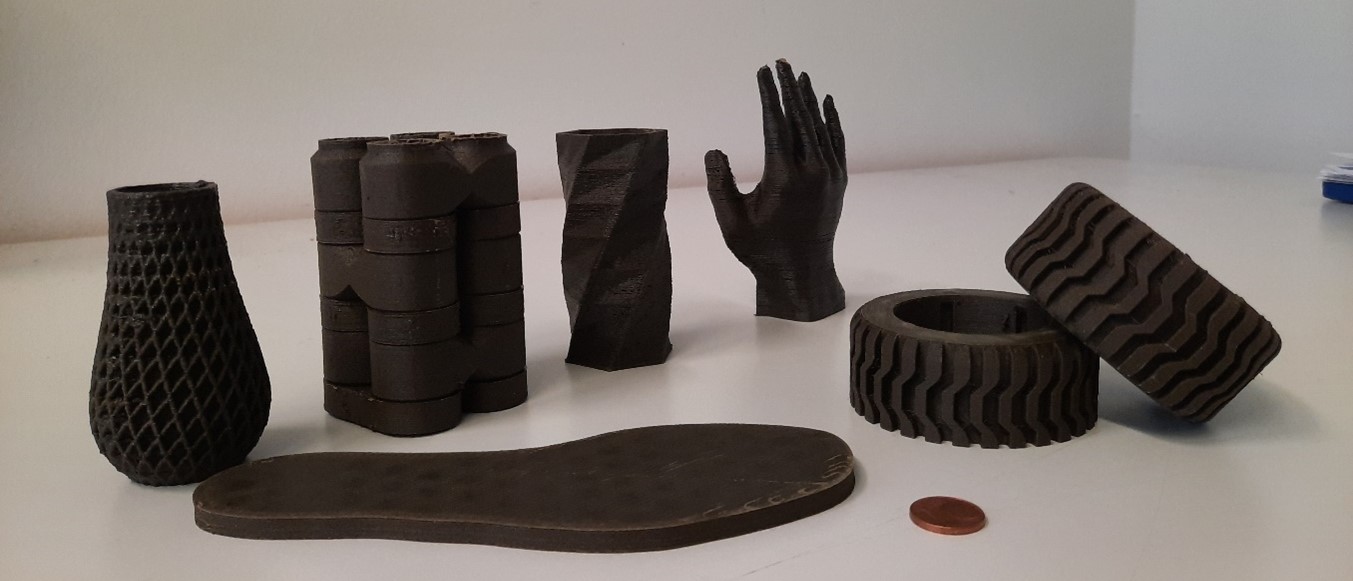

TEXTHAB 3D
shelters and infrastructure by using in-situ resources. TXTHAB-3D project will develop a novel technology and concept for innovative habitation systems for Moon and terrestrial applications. Future missions on the moon will require the development of novel methods to set-up habitats,
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 872336.

Space Radiation Protection Technologies
A state-of-the-art study of space radiation protection technologies for flexible structure systems such as inflatable habitats and spacewalk combinations

DTVC
(Dirty Thermal Vacuum Chamber)
Spartan Space has signed a contract with ESA to manufacture a novel Scenario 3 scale Dirty Thermal Vacuum Chamber (capable of testing space subsystem components at 10-6mbar in the presence of regolith simulant). This system will allow to simulate lunar surface conditions -vacuum, temperature and dust- in an unprecedent scale. The chamber we’re developing will be one of the biggest in its kind on planet Earth.
The project is lead by Spartan Space (France) with the support from HAUX LIFE SUPPORT (Germany), MANNA ELECTRIC (Luxembourg) and LIST (Luxembourg).
See also Press Release 17.Aug 2023
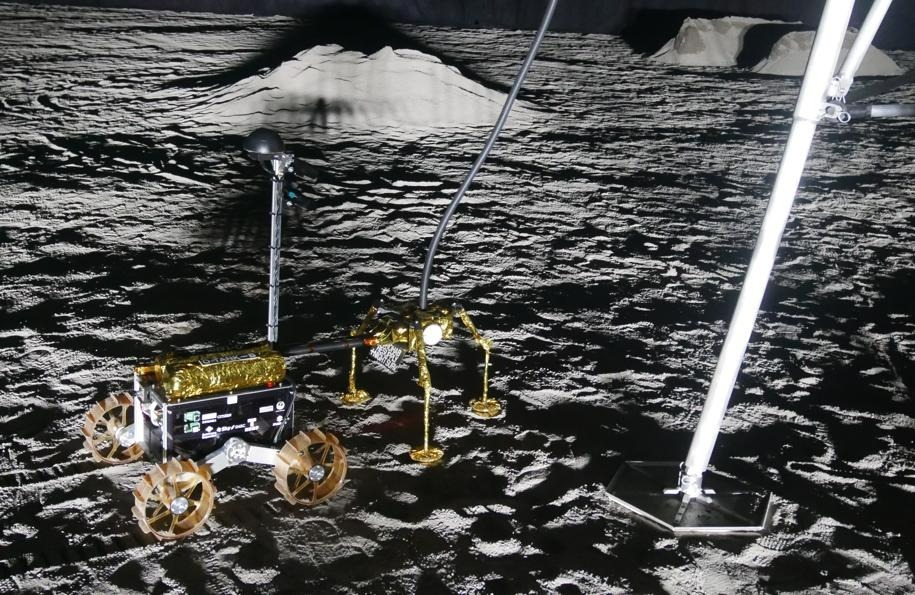
Robotic Docking System
SPARTAN SPACE developed a concept for a robotic docking station for the lunar surface. This system will be used to transfer gases, fluids and power from a robotic vehicle towards a habitat, instrument or facility. Robotic docking can be a useful alternative to transfer of gases, fluids or power over large distances on the lunar surface. The LF mock-up was tested with a robotic vehicle of iSPACE during the ESA ESRIC Lunar Resource Challenge in Luxembourg together with SPARTAN’s partners. The simulation aimed at an in-situ oxygen supply chain simulation in the frame of EURO2MOON.